.bin File Format
Overview
Section titled “Overview”The .bin file format is used to release applications similar to a shellcode payload or a rom dump. It have limits on the program size but should be suited for small to medium programs and games.
This format allows the specification of a load address and provides flexibility for different loading scenarios.
History
Section titled “History”The .bin file format was introduced as a solution to a bug identified in the .elf loader for .hhk files. The initial loader utilized the getaddress function, which incorrectly assumed it could access the entire file. However, this was problematic for larger files that might be split across different sections of flash memory. As a result, when dealing with files larger than a few kilobytes, the loader would often fail because it couldn’t access the necessary parts of the file.
To address this, the .bin format was developed with the following considerations:
-
Direct File Access: The new design used file read functions instead of directly accessing flash memory, ensuring proper handling of files stored in non-contiguous blocks.
-
Flexible Execution: The goal was to allow both plain machine code and
.binfiles to be loaded and executed. If a file contains only machine code, it should still work without needing any specific headers. The optional load address allows for custom loading of.binfiles while maintaining backward compatibility.
Loader Behavior
Section titled “Loader Behavior”The loader checks if the load address starts with 0x8C. If it does, it treats it as a load address; otherwise, it assumes the file contains raw executable code. This approach, while effective, carries some risk—there’s a possibility that a machine code instruction could inadvertently contain 0x8C, leading to potential crashes.
The implementation was aimed to support various combinations of loaders and file types:
- Simple loaders that copy everything to
0x8CFF0000and execute it. - Plain assembly files executed by both simple loaders and the custom loader.
.binfiles with and without load addresses or program descriptions.
You can check the Bin Loader source code on GitHub
File Structure
Section titled “File Structure”The .bin file consists of a header followed by the executable code. The header provides essential information for loading and executing the application.
Header Details
Section titled “Header Details”| Offset | Bytes | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 00 | 2 | D0 01 - Load the address from 0x08 |
| 02 | 2 | 40 2B - Jump to that address |
| 04 | 2 | 00 09 - NOP (No Operation) because the last instruction is a delayed jump |
| 06 | 2 | Unused - reserved for future releases |
| 08 | 4 | Entry point (loaded by the code at offset 00) |
| 0C | 4 | Load address (used by the loader, must start with 8C) |
| 10 | Variable | Name, Description, Author, Version, Null Terminated |
Compatibility
Section titled “Compatibility”For compatibility reasons, if the load address at offset 0x0C does not start with 8C, the default load address is used. Additionally, if the name does not start with an ASCII character, it is also ignored. This ensures that a plain executable code file can also be used without the header information being mandatory.
When a .bin file is loaded, the loader reads the header to determine the entry point and load address. The executable code is then loaded into memory at the specified address, and execution begins from the entry point.
Example
Section titled “Example”Here’s an example of how the .bin file might look:
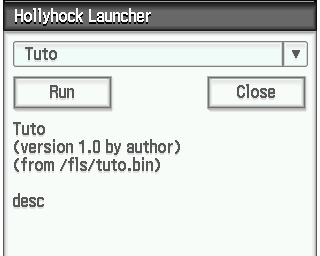
Offset | Hex Data | Description-------|--------------------------|------------------------------------------------00 | D0 01 | Load address from 0x0802 | 40 2B | Jump to the address loaded from 0x0804 | 00 09 | NOP (delayed jump)06 | 00 09 | Unused08 | 8C FF 00 9A | Entry point0C | 8C FF 00 00 | Load address10 | 54 75 74 6F 00 | "Tuto" (Name)15 | 64 65 73 63 00 | "desc" (Description)1A | 61 75 74 68 6F 72 00 | "author" (Author)Here, the sample application “Tuto” with the description “desc” and author “author” is loaded at the address 8C FF 00 00, and execution begins at the entry point 8C FF 00 9A.
It would appear as such like the following launcher :